Computer information technology,computer science,what is software,what is hardware,cit it,computer teachers,Information Technology, Management, mobile, android, iphone new, application to business Management,computer related information, mobile Information Technology, and Urdu tutorials, Urdu course.
Mobile Generations
1st Generation of Mobile phone:
 In First Generation (which is between in 1980s), there was different Mobile communication systems, Which used for analog mobile phones.
In First Generation (which is between in 1980s), there was different Mobile communication systems, Which used for analog mobile phones. The Systems are:
NMT,
AMPS/TACS/ETACS,
Hicap, CDPD, Mobitex, DataTac
2nd Generation of Mobile phone:
In Second Generation (which is between in 1990s), there was different mobile communication systems.
 The Systems are:
The Systems are:GSM, iDEN, D-AMPS, IS-95/cdma one, PDC, CSD, PHS, GPRS, HSCSD, WiDEN, CDMA2000 1XRTT/ IS-2OOO, EDGE (EGPRS
3rd Generation of Mobile phone:
In third Generation (At the beginning of 21st Century), there was more mobile communication systems were developed.
The Systems are: W-CDMA, UMTS(3GSM), FOMA, TD-CDMA/UMTS- TDD, 1XEV-DO/IS-856, TD-SCDMA, GAN/UMA, HSDPA, HSUPA, HSOPA.
W-CDMA, UMTS(3GSM), FOMA, TD-CDMA/UMTS- TDD, 1XEV-DO/IS-856, TD-SCDMA, GAN/UMA, HSDPA, HSUPA, HSOPA. 4th Generation of Mobile phone:
As the limitation of the 3G, people are try to make new generation of mobile communication, this is the 4th generation. This 4G system is more reliable,
 Nowadays, some companies have started developing the 4G communication system, this technology can have a high uplink rate up to 200Mbps, more data can transfer in the mobile phone. So the 4G mobile can have more function such as work as the television. Some telecommunication companies claimed that they would applied this 4G system to the business and it will bring more convenience to people
Nowadays, some companies have started developing the 4G communication system, this technology can have a high uplink rate up to 200Mbps, more data can transfer in the mobile phone. So the 4G mobile can have more function such as work as the television. Some telecommunication companies claimed that they would applied this 4G system to the business and it will bring more convenience to people HISTORY OF MOBILE PHONE
First Invention of Mobile phone
In December 1947, D. H. Ring, a Bell Labs engineer, proposed hexagonal cells for mobile phones. Phil Porter, also of Bell Labs, proposed that the cell towers be at the corners of the hexagons rather than the centers and have directional antennas that would transmit/receive in 3 directions. The technology did not exist then and the frequencies had not yet been allocated. Cellular technology was undeveloped until the 1960s, when Richard Frenkiel and Joel Engel of Bell Labs developed the electronics.
After Some Inventions
Dr. Martin Cooper of Motorola, with the DynaTAC 8000X, first unveiled in 1983. Dr. Cooper made the first analogue mobile phone call on a larger prototype model in 1973.
Mobile Phone?
Mobile phone is a Communication Device, through which we Communicate with others. Nowadays, mobile phone is one of the most essential things of people. It takes much convince for people. The technology of mobile phone is increase rapidly everyday. More and more people are using mobile phone than the world could have ever imagined in the past. It is predicted that by 2005, there will be 1.6 billion mobile phone users world wide. Form 1st generation up to now, people want to build up a mobile.
WHAT IS COMMUNICATION ?
- Communication is the name of giving or receiving information. Communication can be understood as the passing of information in humans, animals, computers, or any other cognitive entity. In a broader sense communication can refer to almost any type of movement, be it matter, energy, force or some effect. Space and time might be the only things that can't themselves be communicated.
- Human communication refers to the social interaction of giving and receiving information for the purpose of not only understanding, but also facilitating social connection. communication allows us to give this information to others for the purpose of enriching life for ourselves and others. when speaking about communication it is very important to be sure about what kind of communication are we speaking about, mainly: what type of things are communicated, between what agents, and with what kind of results. There are many ways or we can say that We have many Technology to communicate with others.
Introduction of files and database storage
-
- A collection of data or information that has a name, called the filename.
- Almost all information stored in a computer must be in a file.
- There are many different types of files: data files, text files, program files, directory files, and so on.
- Different types of files store different types of information. For example, program files store programs, whereas text files store text.
All information on your computer is stored in files. - it may contain a computer program, a word processing document, a photographic image, sounds, a link to a Web page, a video clip, an animation, a spreadsheet.
- DATABASE STORAGE
- A collection of information organized and presented to serve a specific purpose.
- A telephone book is a common database.)
- A computerized database is an updated, organized file of machine readable information that is rapidly searched and retrieved by computer.
- A collection of related information. All the data about a calf crop might be called a database.
SOFTWARE PIRACY
Copyright
A copyright provides its holder the right to restrict unauthorized copying and reproduction of an original expression (i.e. literary work, movie, music, painting, software, mask work, etc.)
Shareware
Shareware (Try before you buy) is a marketing method, not a type of software.
Public Domain
Information in the public domain is open for free use by the public, so public.
A term which is often used to refer to computer software for which the author has released rights to the general public.
WIRELESS MOBILE COMMUNICATION
Communication Technology
Wireless
•Communication use media but without any physical pathway.
•Pass the signal through radio waves.
Bluetooth
A low level bandwidth system use in Mobile phone technology.
It transmit Packet, each packet consist:
Network ID, Device ID, Logical Channel Identifire ID.
This type of network is called PICO NET.
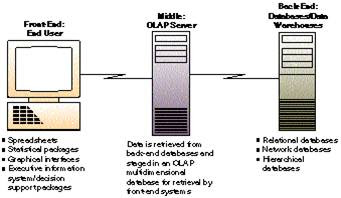
Diagram
What is a Network?
-
- Interconnectivity between computer is called Network:
- The network must have:
- Something to share (Services)
- Physical Pathway (Medium)
- Rules of Communication (Protocol)
Multi User's
Multi-User Operating System
A multi-user Operating System allows for multiple users to use the same computer at the same time and/or different times.
Linux
UNIX
Windows 2000
Multi-Multi Processing Operating System
An Operating System capable of supporting and utilizing more than one computer processor. Below are some examples of multiprocessing Operating Systems.
Linux
UNIX
Windows 2000
Multi-Tasking Operating System
An Operating systems that is capable of allowing multiple software processes to be run at the same time. Below are some examples of multitasking Operating Systems.
UNIX
Windows 2000
Operating System Types
- The winner in the PC market was MS-DOS, Microsoft's Disk Operating System,
- Windows 95 and Windows 98 are actual operating systems on their own.
- Windows Me (Windows Millennium Edition) is an upgrade of Windows 98.
- Windows 2000 is an upgrade of Windows NT rather than of Windows 98.
- Windows XP is an upgrade to Windows 2000. It comes in two versions - Home and Professional.
- Windows CE is for small devices like palmtop and handheld computers.
- The winner in the PC market was MS-DOS, Microsoft's Disk Operating System,
What is an Operating System
-
- It is a core software component of your computer.
- To provide link between user & interface.
- It controls all hardware of a computer.
- It also admit the Peripheral devices.
- Capable to attend PnP devices.
TYPES OF TRANSLATORS
Assemblers
- That generate machine code instructions.
- Use mnemonics when writing source code programs.
- Variables are represented by symbolic names.
- Do not Memory locations as variable name.
- Symbolic code is easier to read and follow.
- Error checking is provided.
- Changes can be made easily incorporated with a re-assembly.
INTERPRETER
- The source code run through a program called an interpreter.
- It translate the code line by line.
- Suspend execution on error.
- Qbasic & Gw-Basic use Interpreter.
COMPILER
- It translate the whole program at once.
- Produce report of errors/ warning after translating whole program.
- Line & Colum also mentioned in report.
- Do not run the program if any of the logical / syntax error exist.
- C , Pascal , & C++ use this technique.
Programming Languages
It is used to write some instruction for computer to take work by user.
1. First Generation ( 1GL ) Machine Language
2. Second Generation ( 2GL ) Basic Assembly Language Turbo Assembler.
3. Third Generation( 3GL ) Gw-Basic, C,C++, Cobol
4. Fourth Generation ( 4GL ) Visual Languages
5. Fifth Generation (5GL) AI Languages LISP,PROLOG
6. Sixth Generation (6GL) Multithread Language Java Language.
Subscribe to:
Posts
(
Atom
)